Explain the Different Phases of the Cell Cycle
For a typical rapidly proliferating human cell with a total cycle time of 24 hours the G 1 phase might last about 11 hours S phase about 8 hours G 2 about 4 hours and M about 1 hour. Now up your study game with Learn mode.
Phases Of The Cell Cycle Article Khan Academy
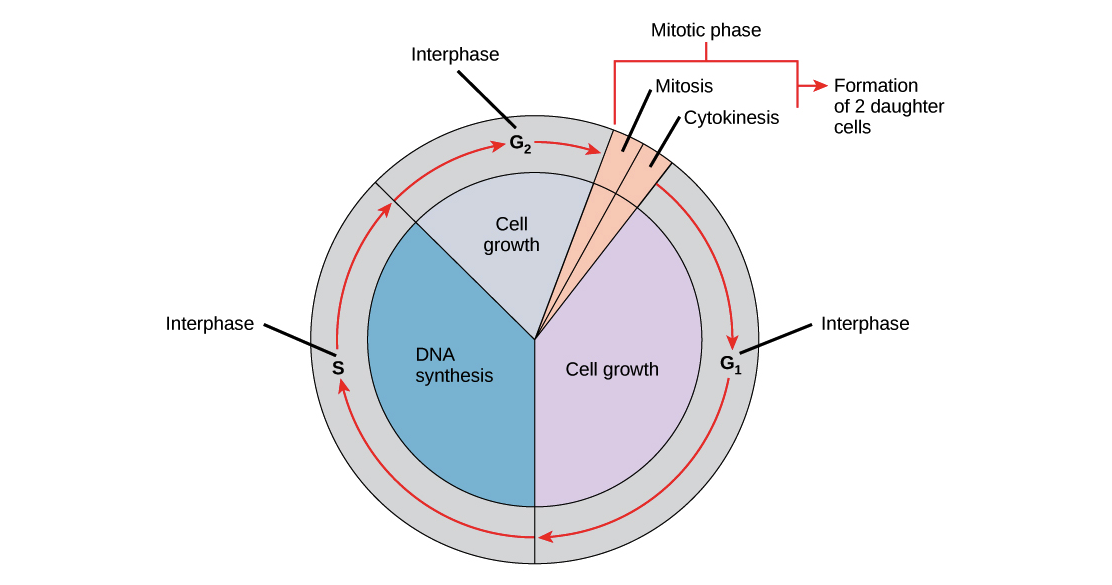
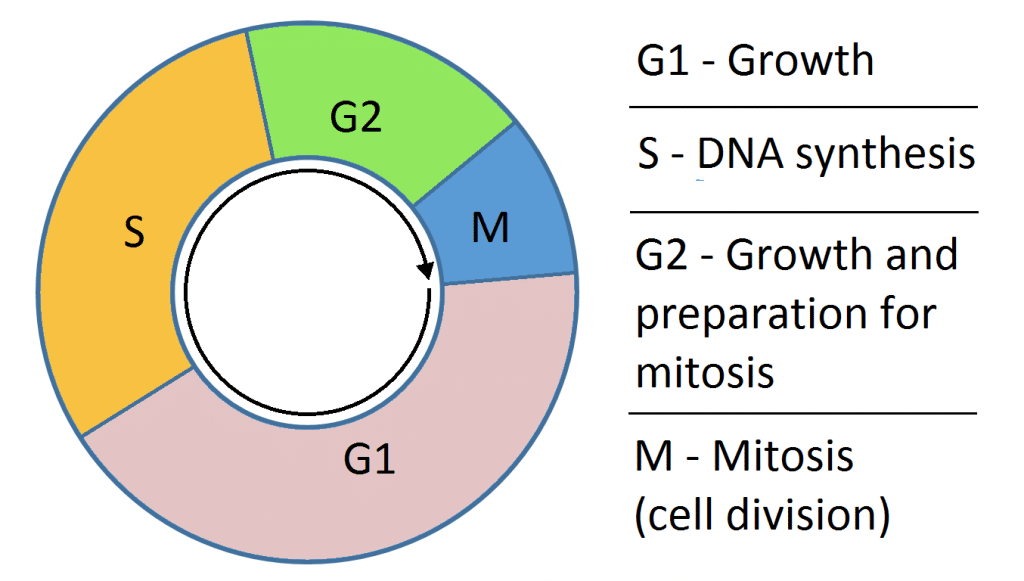
G1 is the stage where the cell is preparing to divide.

. The mitotic phase is divided into four overlapping stages- Prophase Metaphase Anaphase and Telophase. The cell cycle contains six main stages. Protein synthesis happens in this phase.
It has four stages- G1 S G2 and M phase. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. To do this it then moves into the S phase where the cell copies all the DNA.
The results are shown in the table. Other types of cells however can divide much more rapidly. Cell cycle is the name we give the process through which cells replicate and make two new cells.
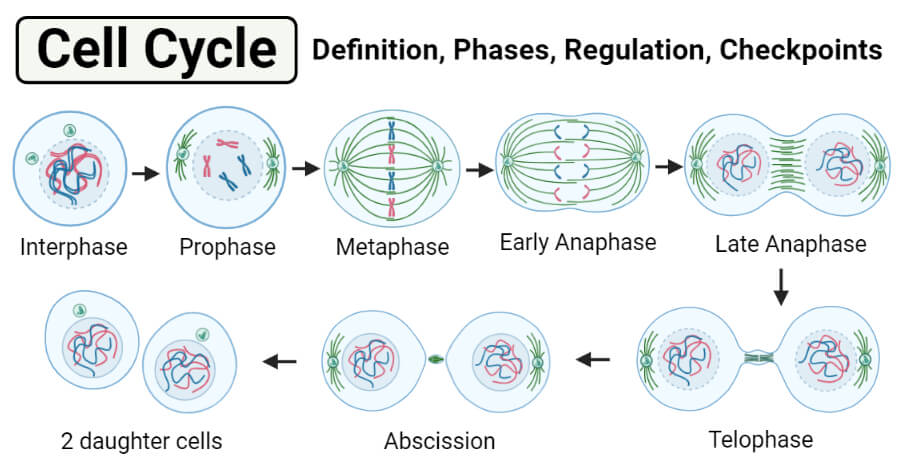
Cell Cycle Definition. Chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes. The number of cells at each stage of mitosis was counted.
The stages of the cell cycle in order are interphase prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. New cells are born through the division of their parent cell producing two daughter cells from one single parent cell. Cyclin B levels are low so MPF level is also low.
This process is known as mitosis and is used to generate new cells. The DNA replication or synthesis occurs during this stage. Centrioles are also copied.
Phases of the Cell Cycle G1 phase. This stage is known as the. The mitotic phase begins with karyokinesis mitosis which consists of five stages.
In anaphase the spindle fibres pull centromere splits and sister chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell. The cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. The cell cycle is the complex sequence of events by which cells grow and divide.
In eukaryotes the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period called interphase. The phases in the reproduction and growth of a cell is known as the cell cycle. Tap card to see definition.
Cyclin B level gradually increases and this binds with more number of CDKs leading to formation of more number of MPF. Click card to see definition. These phases consist of the Mitosis phase M Gap 1 phase G 1 Synthesis phase S and Gap 2 phase G 2The G 1 S and G 2 phases of the cell cycle are collectively referred to as interphase.
The cell is metabolically active and grows continuously during this phase. The cell cycle of cell is called as life cycle The cell cycle is mainly divided into the two major events 1Interphase - This View the full answer. G2 phase Gap 2.
In this section we will discuss the breakdown of the durations of mitosis G1 S phase and G2 for. The duration of these cell cycle phases varies considerably in different kinds of cells. The cell cycle is a four-stage process- G1 gap 1 stage S synthesis phase G2 gap 2 phase and M mitosis phase.
In eukaryotic cells this process includes a series of four distinct phases. While some cells are constantly dividing some cell types are. In prophase DNA coils to form chromosomes nucleus breaksdown and spindle fibres form.
In metaphase chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell and attach to spindle fibre via centromere. The number of cells at each stage is proportional to the time spent at that stage. The five stages of cell cycle are interphase which is in turn classified into G1 S and G2 phase Mitosis also called as the M phase which is further divided into 4 parts prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase and Cytokinesis.
Tumor suppressor genes brake would tend to slow down division when cells are crowded. Answer Drawing and explaination of the key events that occur during the different phases of the cell cycle are as follows. Click again to see term.
Cancer which can be considered as unregulated cell division often results from mutations in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. In order to understand the process let us check the concentration of cyclin B at different stages of cell cycle. The different phases of the cardiac cycle involve.
These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. Cell cycle has different stages called G1 S G2 and M. Tap again to see term.
So S stands for DNA synthesis. Interphase is divided into G 1 S and G 2 phases. Interphase is the resting stage of a cell.
Proto-oncogenes accelerator cyclin allows cells to pass through G2 and divide. The cells that do not undergo further division exits the G1 phase and enters an inactive stage. Three distinct steps of cell cycle.
The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Stage of mitosis - Number of cells Interphase - 123 Prophase - 32 Metaphase - 12 Anaphase - 6 Telophase - 27 One complete cell cycle takes 24 hours. It is sometimes referred to as the cell division cycle for that reason.
For these cells the main concern is not the regulation of the cell cycle which occurs largely in G1 and G2 but rather in the speed of cell proliferation. A cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome synthesizes the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides to form two daughter cells. DNA duplication occurs during S phase S for synthesis which requires 1012 hours and occupies about half of the cell-cycle time in a typical mammalian cell.
Terms in this set 6 Interphase. You just studied 19 terms. The cell grows to its mature size makes a copy of its DNA and prepares to divide into two cells.
G1 Phase Gap 1. After S phase chromosome segregation and cell division occur in M phase M for mitosis which requires much less time less than an hour in a mammalian.
0 Response to "Explain the Different Phases of the Cell Cycle"
Post a Comment